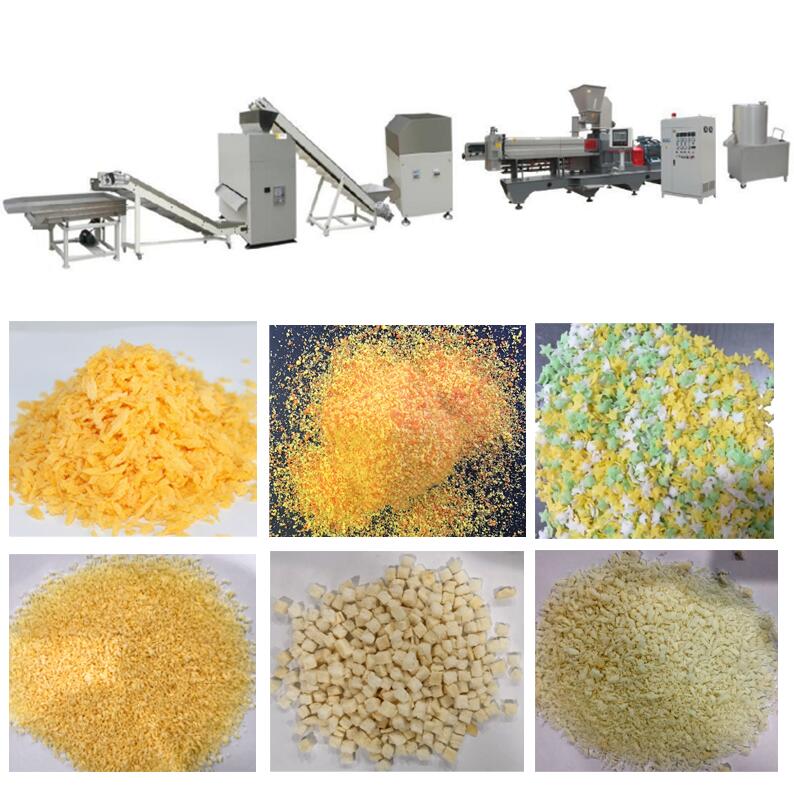
How is TVP Made
Definition
Plant protein meat is also called vegetarian meat, artificial meat, and meat analogs. It is a meat-like food processed using advanced modern food processing technology.
Artificial meat is currently divided into two main types:
One is based on plant protein and is made by adding some auxiliary materials and additives, also called textured vegetable protein (TVP).
The other is to use a specific culture medium to cultivate stem cells in animals to form meat-like tissues, called cell meat or cultured meat.
The biggest problem with cultured meat is that the cost of making this cultured meat is extremely high.
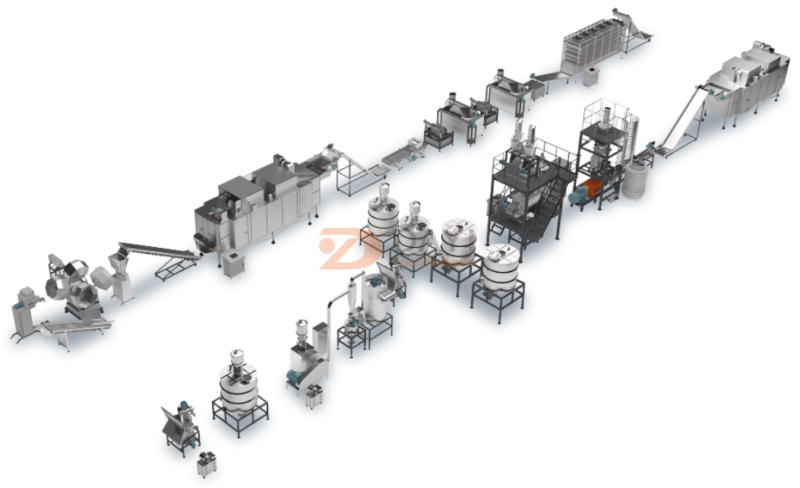
Dayi provides a full set of TVP production line.
Classification
Based on the taste characteristics of TVP products, they are divided into:
Type I: Expanded type:
The pores are loose, and after rehydration, it can be squeezed with fingers and has elasticity similar to that of a sponge.
According to different production processes, the TVP formed can be divided into: more rough tissue with low elasticity type, and finer tissue with good elasticity.
To reduce machine cost, or when quality requirements of soya chunks are not high, the rough texture with low elasticity type can meet the market demand. In some countries or regions with more competition, the fine tissue with large elasticity becomes the trend.
When it is shaped into box shapes or crushed into particle shapes, the finished products TVP is often called soya chunks/badi/nuggets, or soya mince.
Rype 2:High-Moisture Meat Analogue (HMMA)
High Moisture Meat Analogue is extruded with higher moisture.
Store directly in freezers and not need to be rehydration before cooking.
It has a strong fibrous feel and the same texture characteristics as animal muscle.

TVP manufacturing process
1.Expanded type (soya chunks/badi/nuggets/mince, flakes):
Extruder:
Screw length-diameter ratio 28:1
Or 40:1 (according to different texture requirement)
Production of TVP:
Raw material preparation → Raw material mixing (water content 18-25%) → Extrusion molding → Cutting → Drying → Cooling → Packaging
The mouth feel is closer to meat than soya chunks.

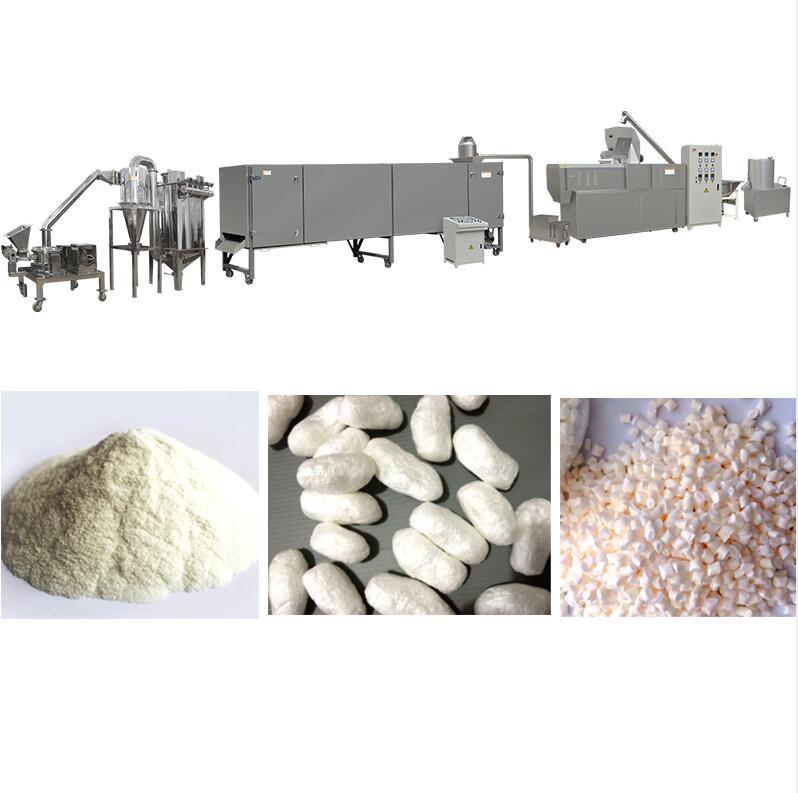
2.High-Moisture Meat Analogue (HMMA)
HMMA Extruder:
Screw length-diameter ratio 50:1
High moisture TVP manufacturing process
Raw material preparation → Raw material mixing (33%) → Extrusion molding → Cutting→ Packaging
Ingredients
The raw materials of TVP produced by extrusion process can be very simple and clean: soya meal.
Soya meal is a byproduct after deoiling of soyabean.
Due to the limitation of the working principle of the extruder, it has strict requirements on the oil content of plant protein–the oil content must be less than 2%.
Therefore, the soybean meal needs to be low-temperature soybean meal (that is, the soya bean is deoiled by chemical extraction rather than extrusion).
In addition, gluten powder, pea protein isolate, etc. are also the best raw materials as they has less oil content too.
Utilisations
The finished TVP can be further processed in different ways to meet different uses.
Kitchen uses: Sold directly as soy nuggets/soya mince. Consumers can directly cook them into different dishes.
After rehydration, stewing, seasoning, sterilization and other processes, it becomes delicious ready-to-eat snack.
After baking and seasoning, it becomes a ready-to-eat crisps.









